Projects
- ArchiSpace: Space architecture in analogue environments
- Robotic Terrain Mapping
- Discretized and Circular Design
- CV- and HRI-supported Planting
- Lunar Architecture and Infrastructure
- Robotic Drawing
- Rhizome 2.0: Scaling-up of Rhizome 1.0
- Rietveld Chair Reinvented
- Cyber-physical Furniture
- Rhizome 1.0: Rhizomatic off-Earth Habitat
- D2RP for Bio-Cyber-Physical Planetoids
- Circular Wood for the Neighborhood
- Computer Vision and Human-Robot Interaction for D2RA
- Cyber-physical Architecture
- Hybrid Componentiality
- 100 Years Bauhaus Pavilion
- Variable Stiffness
- Scalable Porosity
- Robotically Driven Construction of Buildings
- Kite-powered Design-to-Robotic-Production
- Robotic(s in) Architecture
- F2F Continuum and E-Archidoct
- Space-Customizer
CV- and HRI-supported Planting
Year: 2024
Project leader: Henriette Bier
Project team: Henriette Bier, Arwin Hidding, Vera Laszlo, and Micah Prendergast (RB and CoR labs, TU Delft); Dagmar Reinhardt (U Sydney) and Charlotte Firth (UNSW Sydney).
Supervisors / Collaborators / Partners: Vincent Celucci (TU Delft Library)
Funding: 15K
Dissemination: FICTA-2024, UPADSD-2024
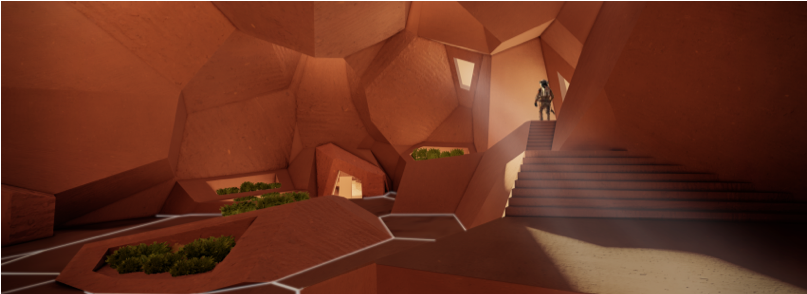
Researchers and practitioners have been exploring the use of robots in terrestrial agriculture to improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and address challenges such as labor shortages and climate change impacts. So far there has not been any documented use of extraterrestrial planting robots, there is, however, theoretical and conceptual exploration regarding the potential use of robots for agriculture in space exploration and colonization efforts. Some hypothetical scenarios include planting robots could be designed to semi- or autonomously plant and tend to crops in controlled environments like greenhouses or hydroponic systems. These robotic agriculture technologies developed for on-Earth applications, are customized for the ESA-funded project, Rhizome, implemented at TU Delft in collaboration with industrial partner, Vertico, for the development of robotic planting in extraterrestrial habitats.
TU Delft in collaboration with U Sydney and UNSW Sydney proposes a CV- and HRI-supported approach that facilitates planting in the hydroponic garden of the rhizomatic habitat. The approach relies on the technology developed at CoR and RB labs using the mobile robotic system of the CoR lab and has been tested in a demo implemented in the TU Delft Library as part of the SHErobots exhibit.